
Walnut Plywood CrossGrain West Wind Hardwood
Bias: The 45˚ angle between lengthwise and crosswise grain. Cutting Strips for Fabric Binding. There might be Fifty Ways to Leave Your Lover, but you can cut strips for binding quilts in only one of three ways: straight grain, cross grain or on the bias. Each way has its own strengths and weaknesses.

Sewing Terms for Beginners Pattern Niche
To cut meat against the grain, first pay attention to the striations in the meat. Lay the meat flat on a cutting board. You'll see that "the grain" appears as small lines going from left to right (or up and down), with some marbling throughout. When slicing the meat, use a sharp knife to cut perpendicular to these lines, or "across the.

Wood grain cross 14 stock photo. Image of hope, stump 3650302
Stability and Durability: Aligning the grain and cross grain correctly contributes to the garment's stability, reducing the risk of stretching or warping over time. Bias Draping: Understanding the grain and cross grain is crucial when working with bias-cut garments. The bias refers to a 45-degree angle to the straight and cross grains.

Seamless end grain wood texture. Cross cut lumber blocks Stock Photo
Cross-grain, with its diagonal cut, poses challenges, but its durability makes it a treasured choice for many. If someone's looking for durability at a modest price, I'd always point them towards cross-grain leather. I hope this deep dive illuminated the wonders of cross-grain leather for you. As always, if you have thoughts, questions, or.
Cross Grain Striations Woodworking Talk
Grain (textile) A close-up image of the grain of blue woven chambray fabric. For woven textiles, grain refers to the orientation of the weft and warp threads. The three named grains are straight grain, cross grain, and the bias grain. In sewing, a pattern piece can be cut from fabric in any orientation, and the chosen grain or orientation will.

Wood Grain Cross Cut Texture, Pine Wood. the Texture of the Wood, Rip
The cross grain is parallel to the cut edge of the fabric (if the fabric shop carefully cut your piece off the bolt). In the photo below, on the right side, you can see the threads fraying where the fabric was cut from the bolt. The bias runs at an angle to the selvage. True bias is at a 45 degree angle to the selvage.

Palm Tree Wood Grain Prices Sale
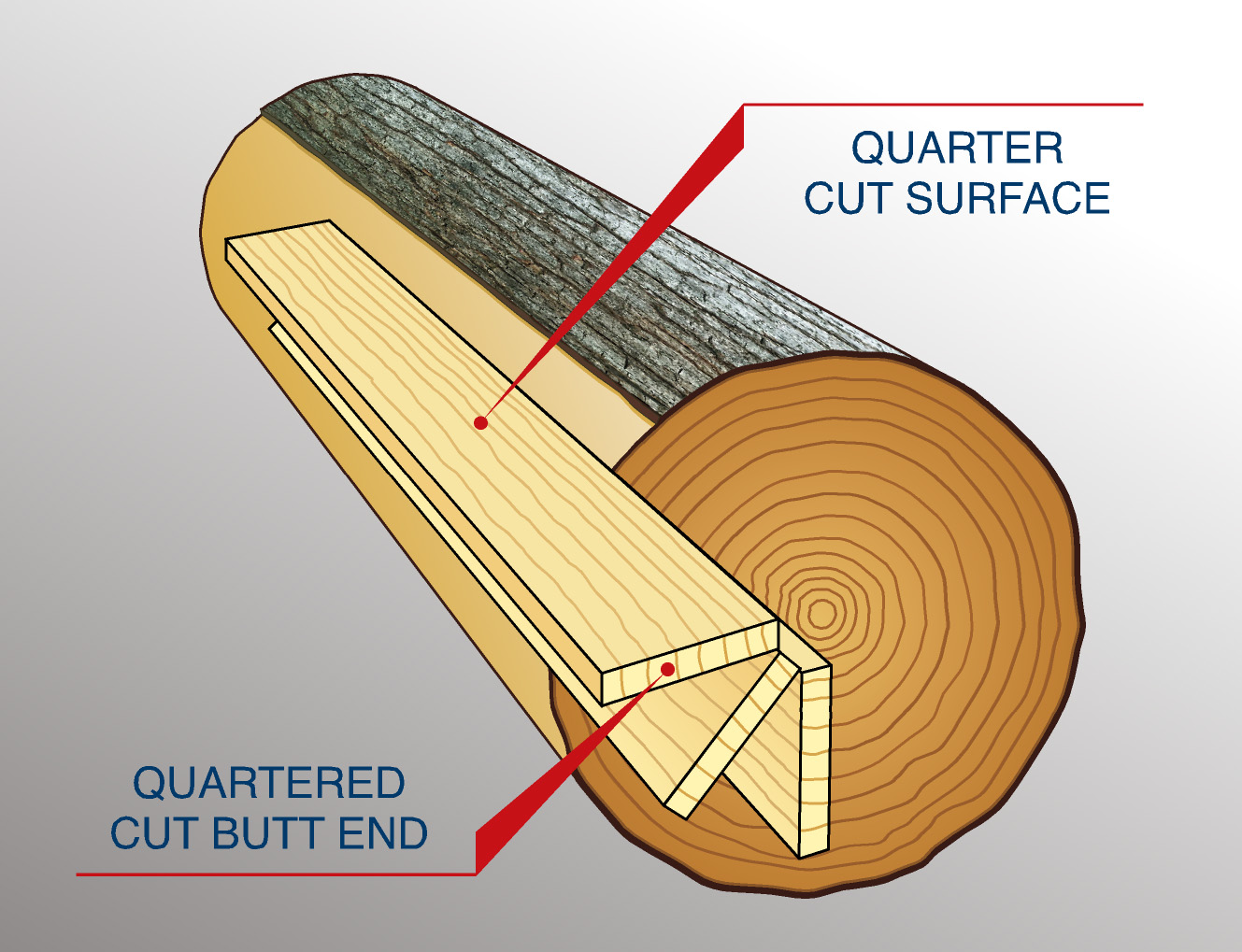
Rip cuts are made parallel to the wood grain, while cross cuts are made perpendicular to it. The blades used for cross-cuts have higher TPI than rip-cut blades. Rip cuts are faster and used for reducing the width and creating straight edges. Cross cuts are smoother and used for cutting large pieces into smaller ones.

Cross Cut Wood Grain Quercast Sawmilling
It depends. I often cut pieces on the cross grain to save fabric or because of the way I want a directional print to run. The differences are usually very subtle, so this works well. However, the more fitted a garment is (think formal dresses or jeans) the more important the grainline becomes.

The Four Most Common Ways to Cut Wood Dream Design DIY
Cross-grain binding has a little more flexibility. If your borders are cut on the straight of grain, cross-grain binding is a good choice. It is probably the most common type of binding used as it is both easy to make and economical use of fabric. To make cross-grain binding, cut your fabric every 2 ½" perpendicular to the selvage.

What is Fabric Grain Understanding Grainline Melly Sews
Do not cut it on the bias as it will stretch out and be strange. If you absolutely must do it, put the fabric on interfacing cut on grain. If pattern piece is to be cut on the bias, cutting it on the grain or cross grain will cause problems as it will not hang right and may stretch strangely. sewingonvintage.

Wood Grain Cross 10 Royalty Free Stock Photography Image 3650187
Types of Fabric Grain . Lengthwise grain refers to the threads in a fabric which run the length of the fabric, parallel to the selvage of the fabric.; Crosswise grain is the threads that run perpendicular to the selvage of the fabric or the cut edge of the fabric as it comes off the bolt.; Bias grain is the thread line that is at a forty-five-degree angle to the lengthwise and crosswise grain.

Wood grain cross 13 stock photo. Image of tree, christian 3650290
In quilting, "crosscut" refers to cutting the fabric at a right angle to the selvage edge of the fabric, which is the finished edge that runs along the length of the fabric bolt. This method of cutting is also known as "cross grain" cutting. When a quilter cuts the fabric in this way, it results in the fabric being cut into strips that.

All About Fabric Grain Blog Oliver + S
This is actually the #1 rule of aligning a sewing pattern to the fabric correctly: Always place the sewing pattern such that the double pointed arrow on the sewing pattern (grainline) is in parallel relation to the selvage edge. The most accurate way to do so is by using a ruler. Measure from one end of the grainline (arrow) to the selvage edge.

All About Fabric Grain Blog Oliver + S
Their layout needs to work as a team with the weave of the fabric. Cutting patterns on the straight of grain is crucial for the garment to hang correctly on the body. It can make the difference between *fabulous* and, well… not so hot. The grain could run in tandem with the main grainline, the cross grain, or even the bias grain.

Cross grain wood flooring. Renovations, Furniture design, Wood floors
Have you ever cut a garment on the cross-grain and felt uneasy about it? Breaking the rules when you know how to do it in the best way can result in the most.
Crossgrain PVC edgebanding « Cantisa
We cut this Croquet Dress on the cross grain to take advantage of the border along the selvedge. Bias Grain. Runs at a 45-degree angle to the length and cross grains. Has a lot of stretch or give. Can be difficult to work with because of the stretch. Bias needs to be handled with care because once it has stretched it can't always recover.